China and AI
The best overall resource on China and AI is from Jeffrey Ding, Assistant Professor of Political Science at George Washington University. See his ChinAI substack. Some takeaways:
- China is behind on AI and it’s unclear whether they have a path to “overtake” the US. AI is a complicated subject and it’s not even obvious what it means to “dominate”. Data is an advantage for some things (e.g. facial recognition) but much depends on the kind of application to which you put that data.
- China is far behind on semiconductors and chips, and machine speed is an important factor in deciding who’s “ahead”.
See his Mar 2018 thesis Deciphering China’s AI Dream
See Also
China’s game plan for the AI race is from the Asymmetric Substack and argues that China is simply using its “bide time” strategy, steadily building its core technologies while waiting for the US to make a mistake.
Chinese grammar detection GrammarGPT Exploring Open-Source LLMs for Native Chinese Grammatical Error Correction with Supervised Fine-Tuning
Alibaba’s Tongyi Qianwen
SenseTime is the world’s largest facial recognition company
also see GPT Implementations
Jon Russell summarizes China’s latest AI regulations:
Still, more are launching: JD.com just unveiled a large language model called ChatRhino link. Finally, The New York Times found Baidu’s Ernie bot performed better than ChatGPT in Chinese but, yeah, it dodged sensitive questions
Baidu claims its ERNIE bot is as good as GPT-4. It can generate video and audio responses
2023-05-17: Kissinger on how to avoid WW3
AI will become a key factor in security within five years.
AI cannot be abolished. China and America will therefore need to harness its power militarily to a degree, as a deterrent.
“And if you then rely entirely on what you can achieve through power, you’re likely to destroy the world.”
Chinese LLM
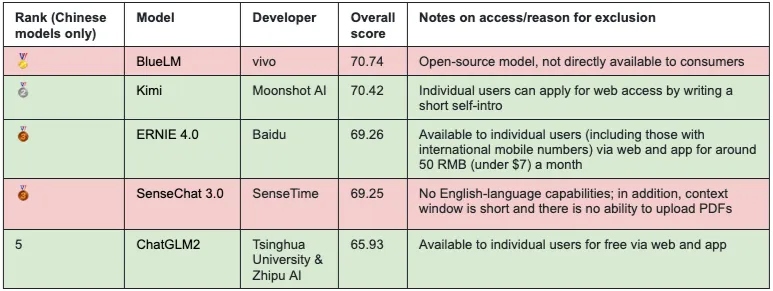
Irene Zhang compares the top Chinese LLMs and concludes the best one is
Moonshot AI’s Kimi — with impressive performance near to GPT-4 in some respects, casting doubt on the claim that Chinese LLMs are, in fact, years behind.
See Paul Triolo ChatGPT and China: How to think about Large Language Models and the generative AI race
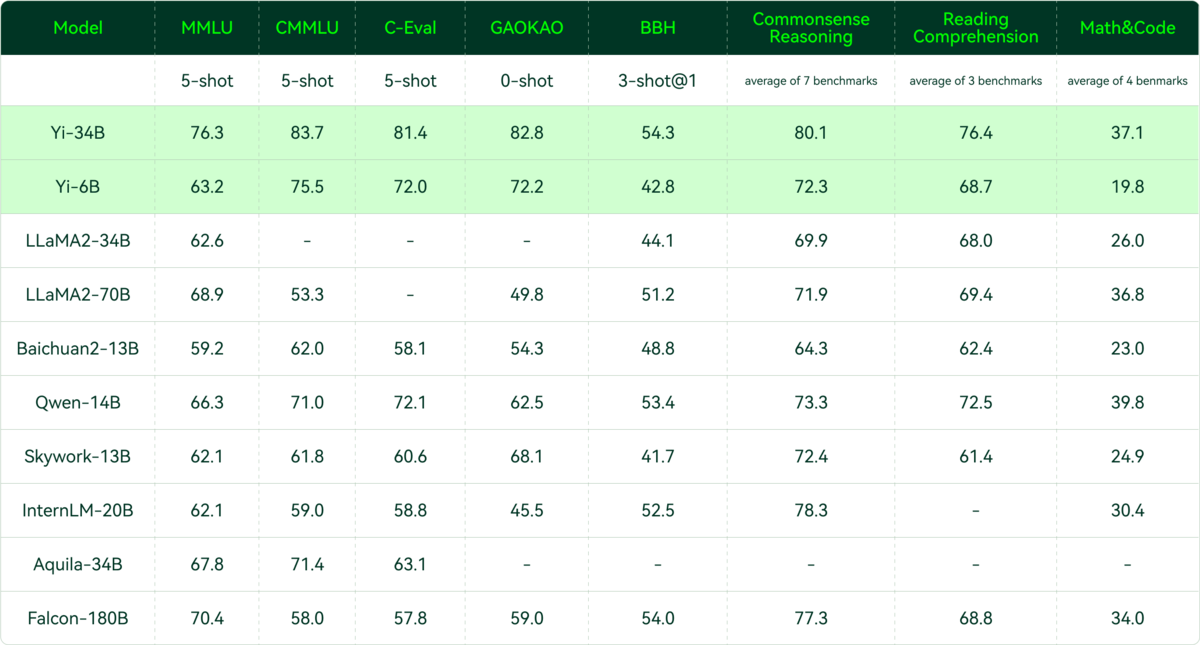
01.AI is Kai Fu Lee’s Startup (see HN)
Regulation
Jeff Ding made a translation of the Blue Paper Report on Large Model Governance (2023): From Rules to Practice:
To file with the algorithm registry, entities have to give detailed information about their algorithm and include other information such as an algorithm safety self-assessment report
The report also gives examples of Baidu and other companies and their implementation of digital watermarking and other techniques intended to follow the spirit of the algorithmic controls
China’s AI Regulations and How They Get Made: A review of a Dec 2022 report1 by Matt Sheehan, a fellow at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, on China’s AI regulatory process.
“China’s approach to AI governance has been uniquely focused on algorithms” as opposed to regulating training data, compute or the ultimate actions taken or enabled by an AI product. This choice, Sheehan argues, is “clearly displayed in Chinese policy discourse around regulations and the decision to make algorithms the fundamental unit for transparency and disclosure via the algorithm registry.”
see Experts react to China’s draft Measures governing AI-generated content services:
Providers must “ensure the data’s veracity, accuracy, objectivity, and diversity”, a very high bar given the way LLMs work.
- API providers are responsible for all content their APIs produce!
- Measures apply to research as well as to products
- Must apply to the CAC for a security assessment before making it available to the public.
- Must allow tagging, to allow tracing content that was AI generated
AI-generated content (AIGC) must comply with “socialist core values”.
Remember, censorship is extra hard for LLMs because, even if you only train on clean censored data, you won’t know how to respond to user input – which may include data that you want to censor. To understand what you should censor requires training on some censored data.
China already has an “algorithm filing system” (算法备案系统 aka the Internet Information Service Algorithm Filing Systems ) that requires developers to conduct security assessments and disclose details about how their algorithms were trained.
cybersecurity company QiAnXin offers consulting services and tools to help with compliance
Implications
China’s technology is likely to evolve in a more vertical manner, rather than the general-purpose chatbot of the US. Your personal robot might be able to respond to your commands but it just won’t be of much use to somebody who wants to talk about politics.
Wired says China is investing heavily in autonomous warfare (drones, robots, etc.) > A report out of Georgetown University in 2021 found that the People’s Liberation Army spends more than $1.6 billion on the technology each year—roughly on par with the US.
China and Medical AI
See Jeff Ding’s summary of a recent AI Medical event:
asked if medical care would be the first batch of industries where GPT lands, Dalei Zhang founder of Airdoc[鹰瞳科技], responded: “Medical care is not the first batch, it is the zeroth batch.”
and
According to VBData estimates, from 2020 to 2025, the compound annual growth rate of China’s medical AI sector will be about 40%, and the total market size will exceed 30 billion RMB by 2025.
(Full Translation (Google Doc))
Chinese hardware
Why Huawei’s 7nm is not that impressive and why it’ll be 20 years till China has world class lithography: The Internet reports that Tsinghua has broken through the lithography technology chokehold
Within 20 years, it is impossible for any country in the world to be able to completely independently build a lithography machine that represents the most advanced level in the world, and the United States is no exception.
China’s Research
Also see The Geography of Retracted Papers for look at how much fraudulent research happens in China.
Other
Georgetown Center for Security and Emerging Technology publishes Translation Snapshot: Chinese AI White Papers : a collection of translations of recent government-authorized reports about Chinese AI.
also see Kissinger on China and AI
Footnotes
What China’s Algorithm Registry Reveals about AI Governance at Carnegie Endowment↩︎